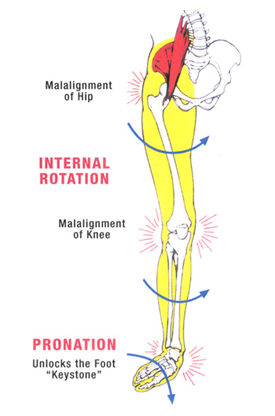
What Does Over-Pronation Mean
Overpronation still continues to be misused and misunderstood. For example, there was a study that got a lot of recent mileage in the mainstream media and the blogosphere that claimed to show that foot pronation was not associated with injury risk. It was intriguing following comments on the study in mainstream media and in social media, especially the parroting of the press release without any critical appraisal. The study actually eliminated the ?overpronators? that were probably at high risk from the study then found that ?overpronation? was not a risk factor. What is more intriguing was that there was another study from around the same time that found the exact opposite. Clearly, the data on ?overpronation? and risk for injury in runners is mixed, so we need to rely on the more formal systematic reviews and meta-analyses of all the data. The most recent one of those concluded that ?overpronation? is just a small risk factor for running injury risk, but it is still statistically significant.
Causes
It is important to identify the cause of overpronation in order to determine the best treatment methods to adopt. Not all treatments and preventative measures will work equally well for everyone, and there may be a little trial and error involved to get the best treatment. A trip to a podiatrist or a sports therapist will help you to establish the cause of overpronation, and they will be able to tell you the best treatments based on your specific degree of overpronation and the cause. Overpronation has many causes, with the most common reasons for excessive pronation listed, low arches, flexible flat feet, fallen arches, gait abnormalities, abnormal bone structure, abnormal musculature, bunions, corns and calluses.
Symptoms
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. Here is a list of some of the common conditions associated with over-pronation in children. Achilles Pain. Ankle pain. Arch Pain. Low back pain. Heel Pain. Knee Pain (Runner's knee and Chondromalecia of the patella) Osgood Schlatter Disease (pain below the knee) Shin Splints (pain in the front of the lower leg) Over-pronation does not necessarily mean your child has "flat feet." Even though children's arches may be relatively high when they lie down or sit, over-pronation may not be seen until your child is standing. A certain amount of pronation is normal. During normal walking or running ("gait cycle"), the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward to absorb shock and adapt to the surface. This gait cycle is even more important if the running surface is uneven.
Diagnosis
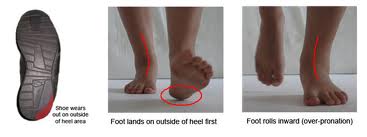
When sitting, an over-pronating foot appears quite normal, i.e. showing a normal arch with room under the underside of the foot. The moment you get up and put weight on your feet the situation changes: the arches lower and the ankle slightly turns inwards. When you walk or run more weight is placed on the feet compared to standing and over-pronation will become more evident. When walking barefoot on tiles or timber floors over-pronation is more visible, compared to walking on carpet or grass.
Non Surgical Treatment
If a young child is diagnosed with overpronation braces and custom orthotics can be, conjunction with strengthening and stretching exercises, to realign the bones of the foot. These treatments may have to continue until the child has stopped growing, and orthotics may need to be worn for life in order to prevent the foot reverting to an overpronated state. Wearing shoes that properly support the foot, particularly the arch, is one of the most effective treatments for overpronation. Custom-made orthotic inserts can also be very beneficial. They too support the arch and distribute body weight correctly throughout the foot. Motion-control shoes that prohibit pronation can be worn, so may be useful for those with severe overpronation. One good treatment is to walk barefoot as often as possible. Not relying on shoes to support the arch will encourage proper muscle use. Practicing yoga can help to correct poor posture and teach you how to stand with your weight balanced evenly across the whole foot.
Prevention
Custom-made orthotics supports not only the arch as a whole, but also each individual bone and joint that forms the arch. It is not enough to use an over-the-counter arch support, as these generic devices will not provide the proper support to each specific structure of the arch and foot. Each pronated foot?s arch collapses differently and to different degrees. The only way to provide the support that you may need is with a custom-made device. This action of the custom-made orthotic will help to prevent heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, calluses, arch pain, and weakness of the entire foot.
Physical Therapy For Severs Disease
Severs disease is by far the most common cause of heel pain in young children, the condition commonly occurs in kids around the age of 10-15 years. Severs is a traction apophysitis in which inflammation of the calcaneal apophysis (growth plate) occurs as a result of overuse or micro trauma. As mentioned severs disease is caused by micro trauma and over use, this can include excessive foot pronation (foot rolling in), tight calf muscles, increase in sporting activities and inappropriate footwear. These all put extra sheering forces on the growth plate leading to aggravation and resultant pain. Signs and symptoms of this include pain on squeezing of the heel, absence of swelling and redness, child describing pain as a dull ache, limping and pain with increased activity.
Causes
The heel bone sometimes grows faster than the leg muscles (including the calf muscles) and tendons (including the Achilles tendon) during the early puberty growth spurt. The different growth rate in these structures can cause lower leg muscles and tendons to become overstretched and tight, which makes the heel less flexible and puts excessive pressure on the heel growth plate. The Achilles tendon, the strongest tendon in the body, attaches to the heel growth plate, and repetitive stress on this structure, especially if it?s already tight, can damage the growth plate, leading to tenderness, swelling, and pain. Activities that involve running or jumping, such as soccer, gymnastics, track, and basketball, can place significant stress on a tight Achilles tendon and contribute to the onset of Sever?s disease. Ill-fitting shoes can also contribute to this health problem by failing to provide the right kind of support or by rubbing against the back of heel. The following factors may increase the likelihood of Sever?s disease in kids or young teens. Wearing footwear that is too narrow in the toe box. Leg length inequality. Obesity or carrying excess bodyweight. Excessive foot and ankle pronation.
Symptoms
A few signs and symptoms point to Sever?s disease, which may affect one or both heels. These include Pain at the heel or around the Achilles tendon, Heel pain during physical exercise, especially activities that require running or jumping, Worsening of pain after exercise, A tender swelling or bulge on the heel that is sore to touch, Calf muscle stiffness first thing in the morning, Limping, A tendency to tiptoe.
Diagnosis
Sever disease is most often diagnosed clinically, and radiographic evaluation is believed to be unnecessary by many physicians, but if a diagnosis of calcaneal apophysitis is made without obtaining radiographs, a lesion requiring more aggressive treatment could be missed. Foot radiographs are usually normal and the radiologic identification of calcaneal apophysitis without the absence of clinical information was not reliable.
Non Surgical Treatment
Fortunately Severs? disease can be treated and prevented through a number of different techniques that have all proven highly effective. The heel will repair itself even without active treatment provided that the suffering foot is given a chance to heal. Typically Severs? disease will take 2-8 weeks, although in many cases it can take longer as the continuous growing of the bone can exacerbate the condition. Podiatrists have an important role in preventing Severs? disease in young athletes, and in treating the condition when it develops so children can get back on their feet as quickly as possible. Generally treatment involves stretching muscles running down to the heel to relieve tension and pain, these include the hamstrings and calf muscles, and these stretching exercises will need to be performed at least 2 or 3 times a day. RICE is a classic method of speeding up the recovery of self-healing injuries like Severs? disease. This involves Rest, the application of Ice to the injury, Compression, and finally Elevation to encourage repaid. These measures can be advised by a trained podiatrist, but it is then up to a child to carry on with regular RICE.
Achilles Tendon Rupture Signs
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is a conjoined tendon composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles with occasional contribution from the plantaris muscle, and it inserts on the calcaneal tuberosity. The plantaris muscle is absent in 6% to 8% of individuals. The Achilles tendon is approximately 15-cm long and is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body. The tendon spirals approximately 90? from its origin to its insertion and this twisting produces an area of stress approximately 2- to 5-cm proximal to its insertion. The tendon has no true synovial sheath; instead it is wrapped in a paratenon. The Achilles tendon experiences the highest loads of any tendon in the body, and bears tensile loads up to 10 times body weight during athletic activities. The tendon most commonly ruptures in a region 2- to 6-cm proximal to its insertion.
The Achilles tendon is a conjoined tendon composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles with occasional contribution from the plantaris muscle, and it inserts on the calcaneal tuberosity. The plantaris muscle is absent in 6% to 8% of individuals. The Achilles tendon is approximately 15-cm long and is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body. The tendon spirals approximately 90? from its origin to its insertion and this twisting produces an area of stress approximately 2- to 5-cm proximal to its insertion. The tendon has no true synovial sheath; instead it is wrapped in a paratenon. The Achilles tendon experiences the highest loads of any tendon in the body, and bears tensile loads up to 10 times body weight during athletic activities. The tendon most commonly ruptures in a region 2- to 6-cm proximal to its insertion.
Causes
Often an Achilles rupture can occur spontaneously without any prodromal symptoms. Unfortunately the first "pop" or "snap" that you experience is your Achilles tendon rupture. Achilles tendon rupture most commonly occurs in the middle-aged male athlete (the weekend warrior who is engaging in a pickup game of basketball, for example). Injury often occurs during recreational sports that require bursts of jumping, pivoting, and running. Most often these are tennis, racquetball, squash, basketball, soccer, softball and badminton. Achilles rupture can happen in the following situations. You make a forceful push-off with your foot while your knee is straightened by the powerful thigh muscles. One example might be starting a foot race or jumping. You suddenly trip or stumble, and your foot is thrust in front to break a fall, forcefully over stretching the tendon. You fall from a significant height. It does appear that previous history of Achilles tendonitis results in a degenerative tendon, which can grow weak and thin with age and lack of use. Then it becomes prone to injury or rupture. Certain illnesses (such as arthritis and diabetes) and medications (such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics) can also increase the risk of rupture.
Symptoms
If the Achilles tendon is ruptured you may experience a sudden pain in the back of your leg, as if someone had kicked you, followed by, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty to stand on tiptoe and push the leg when walking. A popping or snapping sound may be heard when the injury occurs. You may also feel a gap or depression in the tendon, just above heel bone. Ruptures usually occurs in those aged 30 - 70 years, during a sudden forceful push off from the foot. Without proper healing of the tendon, you will have a permanent limp and weakness when using the leg.
Diagnosis
A physician usually can make this diagnosis with a good physical examination and history. X-rays usually are not taken. A simple test of squeezing the calf muscles while lying on your stomach should indicate if the tendon is still connected (the foot should point). This test isolates the connection between the calf muscle and tendon and eliminates other tendons that may still allow weak movement. A word of caution, Achilles tendon rupture is often misdiagnosed as a strain or minor tendon injury. Swelling and the continuing ability to weakly point your toes can confuse the diagnosis. Ultrasound and MRI are tests that can assist in difficult diagnosis. Depending on the degree of injury, these tests can also assist in determining which treatment may be best.
Non Surgical Treatment
You may need to wear a plaster cast, brace or boot on your lower leg for six to eight weeks to help the tendon heal. During this time, your doctor will change the cast a number of times to make sure your tendon heals in the right way. If your tendon is partially ruptured, your doctor will probably advise you to have this treatment instead of surgery. It?s also suitable for people who aren't very physically active. However, there is a greater risk that your tendon will rupture again, compared with surgery. Your doctor will advise you which treatment is best for you. 
Surgical Treatment
Surgical repair is a common method of treatment of acute Achilles rupture in North America because, despite a higher risk of overall complications, it has been believed to offer a reduced risk of rerupture. However, more recent trials, particularly those using functional bracing with early range of motion, have challenged this belief. The aim of this meta-analysis was to compare surgical treatment and conservative treatment with regard to the rerupture rate, the overall rate of other complications, return to work, calf circumference, and functional outcomes, as well as to examine the effects of early range of motion on the rerupture rate.
Prevention
To help prevent an Achilles tendon injury, it is a good practice to perform stretching and warm-up exercises before any participating in any activities. Gradually increase the intensity and length of time of activity. Muscle conditioning may help to strengthen the muscles in the body.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD)
Overview
Adult-acquired flatfoot is a challenging condition to treat. It is defined as a symptomatic, progressive deformity of the foot caused by loss of supportive structures of the medial arch. It is becoming increasingly frequent with the aging population and the obesity epidemic. Patients commonly try to lose weight by exercising to improve the condition. This often leads to worsening of symptoms and progression of the disorder. Early recognition of this complex disorder is essential, if chronic pain and surgery are to be avoided. 
Causes
As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling around the inside aspect of the ankle initially. Later, the arch of the foot may fall (foot becomes flat), this change leads to walking to become difficult and painful, as well as standing for long periods. As the flat foot becomes established, pain may progress to the outer part of the ankle. Eventually, arthritis may develop.
Diagnosis
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction is diagnosed with careful clinical observation of the patient?s gait (walking), range of motion testing for the foot and ankle joints, and diagnostic imaging. People with flatfoot deformity walk with the heel angled outward, also called over-pronation. Although it is normal for the arch to impact the ground for shock absorption, people with PTTD have an arch that fully collapses to the ground and does not reform an arch during the entire gait period. After evaluating the ambulation pattern, the foot and ankle range of motion should be tested. Usually the affected foot will have decreased motion to the ankle joint and the hindfoot. Muscle strength may also be weaker as well. An easy test to perform for PTTD is the single heel raise where the patient is asked to raise up on the ball of his or her effected foot. A normal foot type can lift up on the toes without pain and the heel will invert slightly once the person has fully raised the heel up during the test. In early phases of PTTD the patient may be able to lift up the heel but the heel will not invert. An elongated or torn posterior tibial tendon, which is a mid to late finding of PTTD, will prohibit the patient from fully rising up on the heel and will cause intense pain to the arch. Finally diagnostic imaging, although used alone cannot diagnose PTTD, can provide additional information for an accurate diagnosis of flatfoot deformity. Xrays of the foot can show the practitioner important angular relationships of the hindfoot and forefoot which help diagnose flatfoot deformity. Most of the time, an MRI is not needed to diagnose PTTD but is a tool that should be considered in advanced cases of flatfoot deformity. If a partial tear of the posterior tibial tendon is of concern, then an MRI can show the anatomic location of the tear and the extensiveness of the injury.
Non surgical Treatment
Nonoperative treatment of stage 1 and 2 acquired adult flatfoot deformity can be successful. General components of the treatment include the use of comfort shoes. Activity modification to avoid exacerbating activities. Weight loss if indicated. Specific components of treatment that over time can lead to marked improvement in symptoms include a high repetition, low resistance strengthening program. Appropriate bracing or a medial longitudinal arch support. If the posterior tibial tendon is intact, a series of exercises aimed at strengthening the elongated and dysfunctional tendon complex can be successful. In stage 2 deformities, this is combined with an ankle brace for a period of 2-3 months until the symptoms resolve. At this point, the patient is transitioned to an orthotic insert which may help to support the arch. In patients with stage 1 deformity it may be possible to use an arch support immediately. 
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments don?t work, your doctor may recommend surgery. Several procedures can be used to treat posterior tibial tendon dysfunction; often more than one procedure is performed at the same time. Your doctor will recommend a specific course of treatment based on your individual case. Surgical options include. Tenosynovectomy. In this procedure, the surgeon will clean away (debride) and remove (excise) any inflamed tissue surrounding the tendon. Osteotomy. This procedure changes the alignment of the heel bone (calcaneus). The surgeon may sometimes have to remove a portion of the bone. Tendon transfer: This procedure uses some fibers from another tendon (the flexor digitorum longus, which helps bend the toes) to repair the damaged posterior tibial tendon. Lateral column lengthening, In this procedure, the surgeon places a small wedge-shaped piece of bone into the outside of the calcaneus. This helps realign the bones and recreates the arch. Arthrodesis. This procedure welds (fuses) one or more bones together, eliminating movement in the joint. This stabilizes the hindfoot and prevents the condition from progressing further.